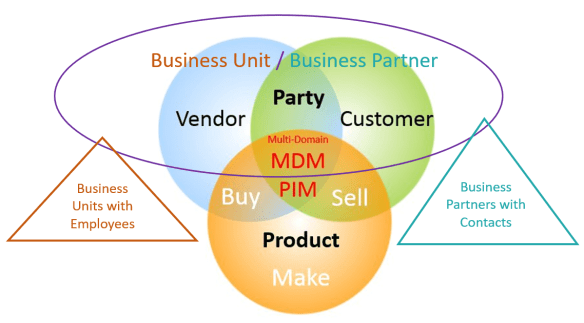
Multi-domain Master Data Management is usually perceived as the union of Customer MDM, Supplier MDM and Product MDM. It is. And it is much more than that.
Customer MDM is typically about federating the accounts receivable in the ERP system(s) and the direct and prospective accounts in the CRM system(s). Golden records are formed through deduplication of multiple representations of the same real-world entity.
Supplier (or vendor) MDM is typically about federating the accounts payable in the ERP system(s) and the existing and prospective accounts in the SRM system(s). A main focus is on the golden records and the company family tree they are in.
Product MDM has a buy-side and a sell-side.
On the buy-side MDM is taking care of trading data for products to resell, in manufacturing environments also the trading data for raw materials and in some cases also for parts to be used in Maintenance, Repair and Operation (MRO). The additional long tail of product specifications may in resell scenarios be onboarded in an embedded/supplementary Product Information Management (PIM) solution.
On the sell-side the trading data are handled for resell products and in manufacturing environments the finished products. The additional long tail of product specifications may be handled in an embedded/supplementary Product Information Management (PIM) solution.

Multidomain MDM does this in a single solution / suite of solutions. And much more as for example:
- Supplier contacts can be handled in a generic party master data structure.
- Customer contacts can be handled in a generic party master data structure
- Besides the direct accounts in CRM the indirect accounts and contacts can in the party master data structure too. Examples of such parties are:
- Influencers in the form of heath care professionals in life science.
- Influencers in the form of architects and other construction professionals in building material manufacturing.
- End consumers in many supply chain B2B2C scenarios.
- Employee records can be handled in a generic party master data structure. The roles of sales representatives and their relation to customers, influencers, product hierarchies and location hierarchies can be handled as well as purchase responsibles and their relation to suppliers, influencers, product hierarchies and location hierarchies can be handled.
- The relation between suppliers and product hierarchies and location hierarchies cand be handled.
- The relation between customers and end consumers and the product hierarchies and location hierarchies can be handled.
- Inbound product information feeds from suppliers can be organized and optimized through Product Data Syndication (PDS) solutions.
- The relation between customer preferences and product information can be handled in Product eXperience Management (PXM) solutions.
- Outbound product information feeds to resellers can be organized and optimized through Product Data Syndication (PDS) solutions.
This site has a list of the most innovative solutions that can either be your multi-domain solution or supplement other solutions as a best-of-breed component. Check the list here.


 Have you ever wondered how to effectively evaluate the return on investment (ROI) of a Product Information Management (PIM) and Master Data Management (MDM) implementation? Then, take a look at some real-life examples. Download the
Have you ever wondered how to effectively evaluate the return on investment (ROI) of a Product Information Management (PIM) and Master Data Management (MDM) implementation? Then, take a look at some real-life examples. Download the 

 MDM solutions have been instrumental in solving core data quality issues in a traditional way, focusing primarily on simple master data entities such as customer or product. Organizations now face new challenges with broader and deeper data requirements to succeed in their digital transformation. Help your organization through a successful digital transformation while taking your MDM initiative to the next level. Download the
MDM solutions have been instrumental in solving core data quality issues in a traditional way, focusing primarily on simple master data entities such as customer or product. Organizations now face new challenges with broader and deeper data requirements to succeed in their digital transformation. Help your organization through a successful digital transformation while taking your MDM initiative to the next level. Download the  Businesses today face a rapidly growing mountain of content and data. Mastering this content can unlock a whole new level of Business Intelligence for your organization and impact a range of data analytics. It’s also crucial for operational excellence and digital transformation. Download the 1WorldSync and
Businesses today face a rapidly growing mountain of content and data. Mastering this content can unlock a whole new level of Business Intelligence for your organization and impact a range of data analytics. It’s also crucial for operational excellence and digital transformation. Download the 1WorldSync and 
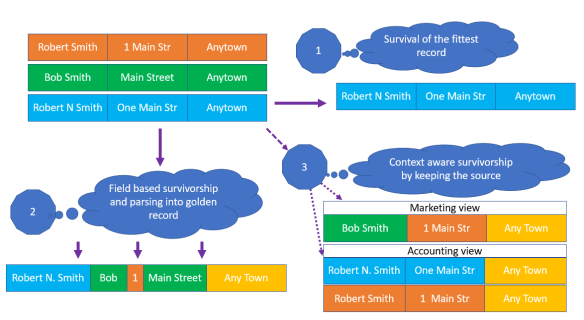
 With persons in private roles a classic challenge is to distinguish between the individual person, a household with a shared economy and people who happen to live at the same postal address. The location hierarchy plays a role in solving this case. This quest includes having precise addresses when identifying units in large buildings and knowing the kind of building. The probability of two John Smith records being the same person differs if it is a single-family house address or the address of a nursing home.
With persons in private roles a classic challenge is to distinguish between the individual person, a household with a shared economy and people who happen to live at the same postal address. The location hierarchy plays a role in solving this case. This quest includes having precise addresses when identifying units in large buildings and knowing the kind of building. The probability of two John Smith records being the same person differs if it is a single-family house address or the address of a nursing home. Organizations can belong to a company family tree. A basic representation for example used in the Dun & Bradstreet Worldbase is having branches at a postal address. These branches belong a legal entity with a headquarter at a given postal address, where there may be other individual branches too. Each legal entity in an enterprise may have a national ultimate mother. In multinational enterprises, there is a global ultimate mother. Public organizations have similar often very complex trees.
Organizations can belong to a company family tree. A basic representation for example used in the Dun & Bradstreet Worldbase is having branches at a postal address. These branches belong a legal entity with a headquarter at a given postal address, where there may be other individual branches too. Each legal entity in an enterprise may have a national ultimate mother. In multinational enterprises, there is a global ultimate mother. Public organizations have similar often very complex trees. Products are also formed in hierarchies. The challenge is to identify if a given product record points to a certain level in the bottom part of a given product hierarchy. Products can have variants in size, colour and more. A product can be packed in different ways. The most prominent product identifier is the Global Trade Identification Number (GTIN) which occur in various representations as for example the Universal Product Code (UPC) popular in Orth America and European (now International) Article Number (EAN) popular in Europe. These identifiers are applied by each producer at the product packing variant level.
Products are also formed in hierarchies. The challenge is to identify if a given product record points to a certain level in the bottom part of a given product hierarchy. Products can have variants in size, colour and more. A product can be packed in different ways. The most prominent product identifier is the Global Trade Identification Number (GTIN) which occur in various representations as for example the Universal Product Code (UPC) popular in Orth America and European (now International) Article Number (EAN) popular in Europe. These identifiers are applied by each producer at the product packing variant level.