This site is a presentation of the best available Master Data Management (MDM), Product Information Management (PIM) and Data Quality Management (DQM) solutions. However, behind the technology there are people who is working hard to bring the best tools to live, break into the market and cover new land.
Semarchy was one of the first disruptive MDM solutions to join the list and FX was one of the first employees to join Semarchy.
 FX, what was your path into Master Data Management?
FX, what was your path into Master Data Management?
It started with Data Integration. Back in 2000, we designed a data integration product called “Sunopsis”. It was the first solution to use an E-LT architecture. In fact, we created that acronym as a “smart data geek” joke, and it is now an established marketing buzzword. The product was acquired by Oracle and is still on the market under the Oracle Data Integrator name. I was Product Manager for Sunopsis and Oracle Data Integrator. As such I was exposed to the challenges of integration (real-time vs. batch, EAI vs. ETL, data quality, performance, etc.). Governance and MDM were not yet trendy terms, but we had the idea of a technical “Active Data Hub”, managed at the integration layer, to share high quality data between systems.
Semarchy was founded in 2011. How did the MDM market look like then?
A vast plain with two large circles of massive monoliths, namely the Customer Data Hub (CDH) and Product Information Management (PIM) verticals. Some of them were ironically sold by the same vendors who had failed to properly manage customer and product data in operational systems (CRMs, ERPs, etc.). When we looked at the market, we realized that there was room for domain-agnostic platforms to support customer, product, and every other domain.
The market was also a graveyard of failed projects. The reasons why so many projects ended up there were suspected (gigantic project scopes with insanely large timeframes, lack of agility and business involvement, etc.) but never clearly stated.
You have been in the forefront of introducing Semarchy. What have been the most difficult challenges in breaking into the market?
Building the platform was a challenge, but education was the hardest part. When you tell people that you know why they have failed or will fail, and you have a solution for a better outcome, they are not really willing to listen. We had to educate people with sound messages: “Yes sir, data quality is part of master data management”, “Start small and grow your initiative”, “Involve the business all along”.
Another challenge was the multiple number of shiny new trends and buzzwords popping up in the data space. Big data, cloud, graph, digital transformation, and now AI? Pick your favorite! Data management, governance, quality or workflows look very dull in comparison. The good thing is good practitioners know that these are prerequisites to get things done correctly.
Now that Semarchy has become an established player on the MDM market, what is the next move?
Since our inception, we’ve always believed in a single platform to solve all master data management issues. This all-in-one solution is still a dream for most companies, who struggle with four or five tools to manage their data. We are now ahead of that with our next move: extending our platform to be the end-to-end Intelligent Data Hub™. This includes new capabilities such as:
- Data Discovery: Profiling data sources and learning about existing critical data assets.
- Integration of any applications and leveraging any data source or service to enhance the enterprise data.
- Governing the data hub by defining and enforcing business terms, processes, rules, policies, etc.
- Managing data using apps designed for data champions and business users, with built-in data quality, match and merge, workflows, generated from the governance definitions and decisions.
- Measuring the efficiency of the operations and the relevance of the governance choices using dashboards, KPIs and metrics based on data from the data hub or from external data sources.
Can you tell something more about how the Intelligent Data Hub is extending the MDM concept?
MDM is mainly about managing the domains core data assets (reference, customer, product, etc..) with data quality, match/merge and stewardship workflows. The data hub extends this idea in multiple directions:
- It extends the scope of data available via the data hub beyond core master data, for example by eventually including transactional data and interactions to provide 360° views.
- It takes an end-to-end approach for the data management initiative: from data governance, data onboarding with data discovery, profiling and cataloguing, down to the assessment of the value delivered with dashboards and KPIs.
- It transparently opens the initiative to the whole enterprise. All business users become full members of the initiative via the data governance, data management and measurement channels. In short, the Intelligent Data Hub transforms every stakeholder in the organization into a data champion.
If you should have done something differently in Semarchy’s route to where you are now, what would that have been?
Go to the cloud from the beginning! Our platform is now available on major cloud platforms. If I had to do it again, I would have shipped the first version on premises *and* in the cloud.


 Data Matching
Data Matching 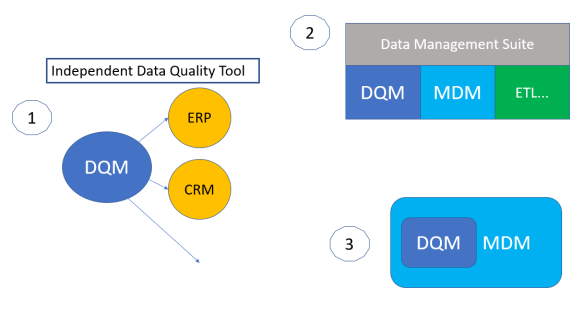
 RDM solutions may offer this functionality around the reference data:
RDM solutions may offer this functionality around the reference data: FX, what was your path into Master Data Management?
FX, what was your path into Master Data Management?