An often-requested capability in Master Data Management (MDM) and Data Quality Management (DQM) is data enrichment from – and verification against – third-party data providers. The data providers can be government data providers, commercial data providers and open data providers.
The two most common used scenarios are:
- Data enrichment from – and verification against – business directories
- Verification against – and enrichment from – address directories
Business directory integration
Integration with business directories is done with party master data as B2B customers and suppliers. The aim is often to enrich already gathered internal master data with external data such as:
- Industry sector codes as SIC or NACE codes
- Company family trees
- Credit worthiness supporting data
Sometimes you may also want to (conditionally) overwrite – or supplement – internal gathered data such as:
- Company name
- Addresses
- Phone numbers
You may also want to verify that a business exists and catch when a business dissolve.
Integration can be done with:
- Global business directories, where Dun & Bradstreet is the most prominent. The advantage here is a uniform integration point and data structure.
- National directories for each country often supplied by a government body. The advantage here is localized data fit for national requirements and optimal freshness.
Address verification
Verifying a postal address – and translating it into a standard format – is done with location master data that most often are part of party master with emphasis on B2C customer data.
Also, in this case there are global versus national options.
Some MDM / DQM providers have their own global services. Examples are Informatica, who acquired the service called Address Doctor, and IBM. Other MDM / DQM providers utilize the service called Loqate. The advantage here is a uniform integration point and data structure.
In many countries there are also national services that provides richer and localized data with optimal freshness. The richness may be multi-language versions, granular structures feasible in that country and property data such as which kind of building that exist on that address.
A common enrichment type is also getting the geocodes related to a postal address.
Your requirements
Your prioritization of business directory integration and address verification is part of the selection criteria here on the site in the Select your solution service.


 Data Matching
Data Matching 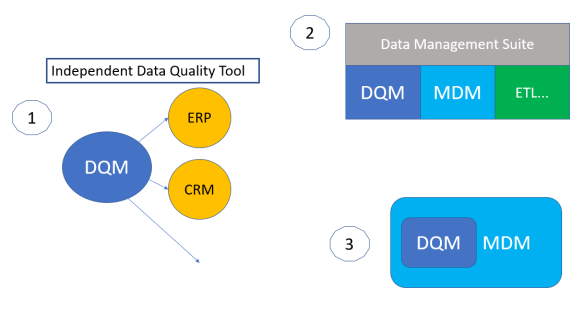
 RDM solutions may offer this functionality around the reference data:
RDM solutions may offer this functionality around the reference data: